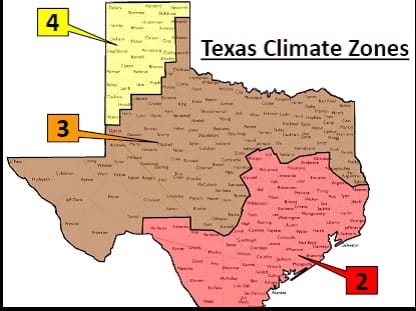
Texas is divided into three climate zones according to the 2018 IECC:
Zone 2 – Southern Texas, including Houston, Austin, San Antonio, and the Gulf Coast
Zone 3 – Central Texas, including Dallas-Fort Worth and surrounding areas
Zone 4 – Northern Texas, including Amarillo, Lubbock, and parts of the Panhandle
It is important to use the correct insulation and window performance values based on your climate zone.
—
The following insulation values are required for compliance with the 2018 IECC in Texas:
| Building Component | Zone 2 | Zone 3 | Zone 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ceilings | R-38 | R-49 | R-60 |
| Walls | R-13 | R-20 or R-13+5 | R-20 or R-13+5 |
| Floors | R-13 | R-19 | R-19 |
| Slab Insulation | Not Required | R-10 (2 ft) | R-10 (2 ft) |
For wood-frame walls, builders can choose between R-20 cavity insulation or R-13 cavity insulation with R-5 continuous insulation.
—
All windows and doors must meet the U-factor and SHGC (Solar Heat Gain Coefficient) limits for their respective climate zones:
| Climate Zone | U-Factor (Max) | SHGC (Max) |
|---|---|---|
| Zone 2 | 0.40 | 0.25 |
| Zone 3 | 0.35 | 0.25 |
| Zone 4 | 0.32 | 0.40 |
SHGC requirements apply only to windows, skylights, and glass doors in Climate Zones 2 & 3 to reduce heat gain.
– Windows in Climate Zone 4 do not have a maximum SHGC requirement, allowing for more solar heat gain in colder areas.
—
Ducts located in unconditioned spaces (attics, crawlspaces) must have a minimum of R-8 insulation.
– If ducts are buried in attic insulation, the total insulation value (including the ceiling insulation above and below the ducts) must be at least R-19.
– If ducts are inside conditioned space, no additional insulation is required.
—
Builders in Texas have three options for energy code compliance:
1. Prescriptive Path – Follow the exact insulation, window, and duct insulation requirements listed above.
2. Performance Path – Use energy modeling to show that the building performs as well as a prescriptive-code building.
3. HERS Index Path – Achieve a Home Energy Rating System (HERS) score that meets Texas standards.
To determine the best compliance method, consult with a certified energy rater or building inspector.
Texas follows the 2018 IECC statewide, but local jurisdictions may enforce stricter energy codes. Cities like Austin, Dallas, and Houston have adopted additional amendments to the IECC.
Always check with your local building department for any additional requirements.
—
For official Texas energy code guidelines, visit the [Texas State Energy Code Website](https://www.tdlr.texas.gov).
The IRC/IECC divides the country into 8 climate zones that are used to apply different insulation and fenstration requirements.
Zone 2 – Southern Texas, including Houston, Austin, San Antonio, and the Gulf Coast
Zone 3 – Central Texas, including Dallas-Fort Worth and surrounding areas
Zone 4 – Northern Texas, including Amarillo, Lubbock, and parts of the Panhandle